본 게시물은 University of Arizona의 Prof. J. Scott Tyo의 OPTI512R 강의를 보고 정리한 내용입니다.
전공자가 아닌 만큼 부정확한 정보가 포함되어 있을 수 있습니다.
부정확한 정보가 있다면 알려주시면 감사하겠습니다.
Effect of Aberrations
아래 그림에 묘사된 optical imaging system의 diffraction effect에 대한 system view를 고려해보자. 이전에 우리는 object position $(x_o, y_o)$에서 발생하는 entrance pupil에 incident 하는 spherical wave를 image position $(M_{x_o}, M_{y_o)$에 focus 한 exit pupil을 떠나는 spherical wave로 convert 하는 ideal diffraction-limited optical system을 고려하였다.
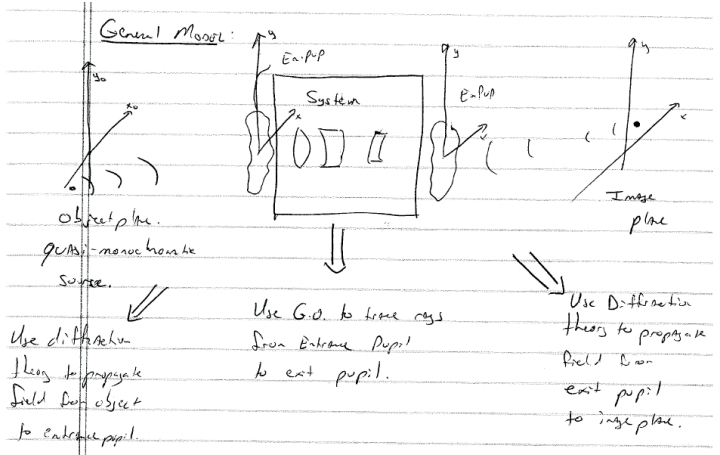
우리는 Real optical system이 exit pupil을 떠나는 wavefront의 sphericity로부터 deviation을 describe 하는 wavefront aberration이 있다는 것을 알고 있다. OPL aberration function $W(x,y; x_o, y_o)$를 define한다. 이는 여기에서 pupil coordinate $(x,y)$와 object coordinate $(x_o, y_o)$의 function으로 denote된다. sphericity로 부터의 이러한 deviation은 $f(x)$의 exit pupil의 $(x,y)$ position에 다음과 같은 additional phase를 부여한다.
$$\phi_{aberr} = {2\pi \over \lambda} W(x,y; x_o, y_o)$$
1. Coherent Systems
Lens, Grating 그리고 다른 transmissive object에 대한 우리의 discussion에 따라, 우리는 aberration의 effect를 phase plate로 다음과 같이 describe 할 수 있다.
$$t_{aberr} = e^{j{2\pi \over \lambda}}W(x,y; x_o, y_o)$$
그리고 modified exit pupil은 다음과 같아진다.
$$P(x, y; x_o, y_o) = P(x, y)e^{j {2\pi \over \lambda}} W(x,y;x_o,y_o)$$
이전 discussion에서 우리는 binary pupil에 의해 describe 된 low-pass(혹은 band-pass) filter의 측면에서 coherent transfer function을 describe 하였다. 이제 $P(x,y)$가 제공하는 Amplitude-only filter와 $exp\{(2\pi/\lambda)W(x, y; xo, yo)\}$가 제공하는 Phase-only filter가 있다. 이제 coherent transfer function은 다음과 같다.
$$H(\xi,\eta) = P(−\lambda d_i\xi, \lambda d_i \eta) = P(−\lambda d_i\xi, −\lambda d_i \eta)e^{j {2\pi \over \lambda}} W(−\lambda d_i \xi,−\lambda d_i \eta;x_o,y_o)$$
마찬가지로, coherent impulse response는 다음과 같다.
$$\tilde h (x,y) = \mathcal{F} \{ H(\xi, \eta)\}$$
이는 aberration function W의 form에 따라 계산하기 쉽지 않을 수 있다. Aberration의 effect는 phase distortion을 유발하는 것이며, 이는 image quality에 매우 해로울 수 있다.
2. Incoherent System
이제 Aberration이 Incoherent system의 OTF에 미치는 effect를 살펴보도록 하자. 우리는 binary pupil(즉, $P(x,y) = 1 or 0$)에 대해 OTF가 다음과 같이 compute 될 수 있음을 알고 있다.
$$H(\xi,\eta) = {A_{overlap}(\xi,\eta) \over A} $$
Aberration의 경우 numerator의 overlap integral에 대한 이러한 aberration의 (complex) effect를 고려해야 하고, 위 수식은 다음과 같이 변한다.
$$\mathcal{H}(\xi, \eta)=\frac{\iint_{A(\xi, \eta)} \exp \left\{j \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda}\left[W\left(-\lambda d_{i} \xi^{\prime},-\lambda d_{i} \eta^{\prime}\right)-W\left(-\lambda d_{i}\left(\xi^{\prime}-\xi\right),-\lambda d_{i}\left(\eta^{\prime}-\eta\right)\right)\right]\right\} d \xi^{\prime} d \eta^{\prime}}{A}$$
Numerator는 이제 aberration이 있는 transfer fucntion의 autocorrelation function이 된다.
우리는 위 수식을 직접 계산하여 Aberration이 specific real optical imaging system에 미치는 effect를 확인할 수 있다. 그러나 우리는 모든 system에 적용되는 aberration의 effect에 대한 몇 가지 general statement를 만들 수 있다. Schwarz inequality로부터 우리는 다음이 성립함을 알 수 있다.
$$\left|\iint X Y d \xi^{\prime} d \eta^{\prime}\right| \leq \sqrt{\iint|X|^{2} d \xi^{\prime} d \eta^{\prime} \iint|Y|^{2} d \xi^{\prime} d \eta^{\prime}}$$
우리의 case에서 funciton $X$와 $Y$는 다음과 같다.
$$\begin{aligned}
X\left(\xi^{\prime}, \eta^{\prime}\right) &=\exp \left\{j \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda} W\left(-\lambda d_{i} \xi^{\prime},-\lambda d_{i} \eta^{\prime}\right)\right\} \\
Y\left(\xi^{\prime}, \eta^{\prime}\right) &=\exp \left\{j \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda} W\left(-\lambda d_{i}\left(\xi^{\prime}-\xi\right),-\lambda d_{i}\left(\eta^{\prime}-\eta\right)\right)\right\}
\end{aligned}$$
그리고 $|X| = |Y| = 1$이다. 이 정보를 통해 우리는 위 수식을 다음과 같이 정리할 수 있다.
$$\left|\iint X Y d \xi^{\prime} d \eta^{\prime}\right| \leq A_{\text {overlap }}(\xi, \eta)$$
그리고 우리는 다음의 매우 중요한 결과를 얻었다.
$$\left|\mathcal{H}_{\text {aberrations }}(\xi, \eta)\right| \leq \mid \mathcal{H}_{d l}(\xi, \text { eta }) \mid$$
위 수식은 aberration의 effect가 optical system의 MTF를 uniformly reduce 하여 모든 spatial frequency에서 contrast를 감소시키는 것으로 해석할 수 있다.
3. Example : Focus error
가장 간단한 example로 focus가 약간 벗어난 system에 대한 defocus error effect를 살펴보도록 하자. defocus error를 quantify 하기 위해 우리는 다음을 정의할 것이다.
$$\frac{1}{d_{o}}+\frac{1}{d_{i}}-\frac{1}{f}=\frac{\epsilon}{d_{i}}$$
이때, $\epsilon$은 small number이고, 우리는 다음을 얻는다.
$$\tilde{h}\left(x_{i}, y_{i} ; x_{o}, y_{o}\right)=\mathcal{F}\left\{\operatorname{rect}\left(\frac{-\lambda d_{i} \xi}{L}, \frac{-\lambda d_{i} \eta}{L}\right) e^{-j \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda d_{i}} \epsilon\left(\xi^{2}+\eta^{2}\right)}\right\}$$
우리는 width L의 rectangular aperture를 가정할 것이다. 이 coherent impulse response에 따른 MTF는 다음과 같이 주어진다.
$$\mathcal{H}(\xi, \eta)=\operatorname{tri}\left(\frac{\xi}{2 \xi_{o}}\right) \operatorname{tri}\left(\frac{\eta}{2 \eta_{o}}\right) \operatorname{sinc}\left(\frac{8 w}{\lambda} \frac{\xi}{2 \xi_{0}}\left(1-\frac{|\xi|}{2 \xi_{0}}\right)\right) \operatorname{sinc}\left(\frac{8 w}{\lambda} \frac{\eta}{2 \eta_{0}}\left(1-\frac{|\eta|}{2 \eta_{0}}\right)\right)$$
위 수식은 aperture의 edge를 pass 하는 ray에 대한 maximum path length error인 $w = \epsilon L^2/(8d_i)$ 및 $\xi_0 = \eta_0 = L/(2\lambda d_i)$가 coherent transfer function의 cutoff frequency인 다음 quantity로 parameterize 된다.
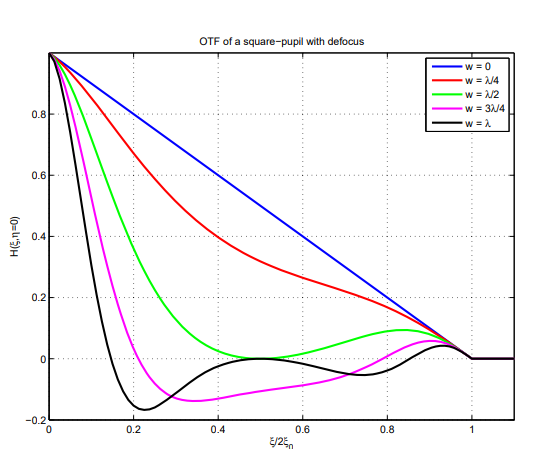
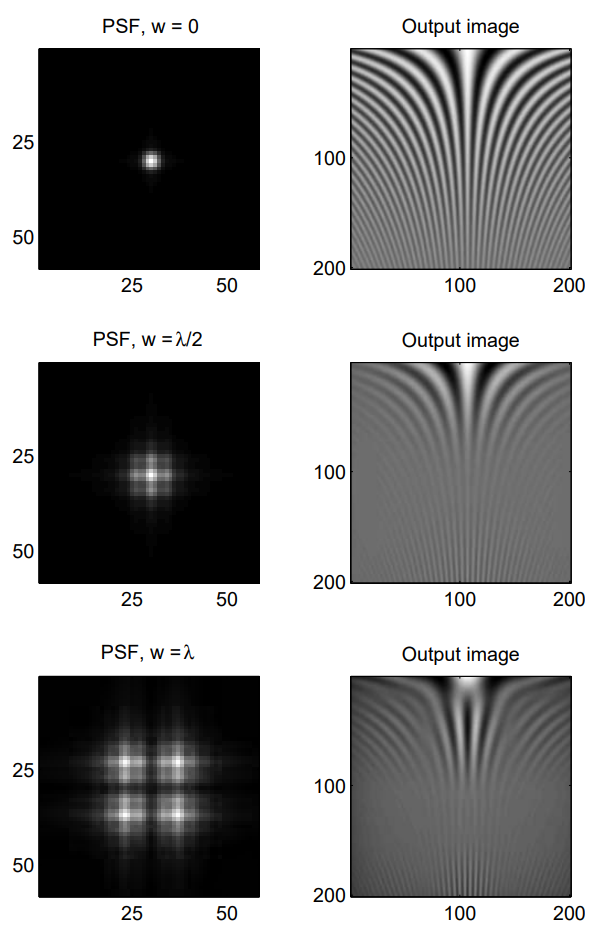
OTF는 위 그림에 plot 되어 있다. 해당 PSF의 x-axis를 따른 cross section이 아래 그림에 표시된다.
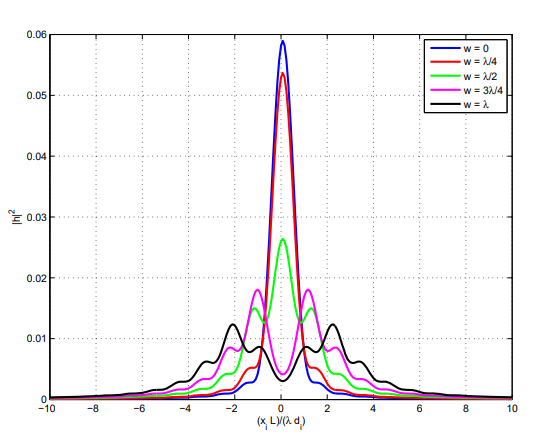
우리는 OTF와 PSF의 몇 가지 매우 흥미로운 Property를 발견하였다. 첫째로 우리는 0.5-wave의 defocus aberration에 대해 MTF가 0인 frequency가 존재한다는 것을 알 수 있다. 위 그림의 해당 PSF를 검토해 보면 그 원인을 파악할 수 있다. $w < \lambda/2$의 경우 PSF에 secondary peak가 나타난다. 이는 certain frequency의 periodic signal과 interact 하여 정확히 0의 MTF를 제공한다. 또한 $w > \lambda/2$의 경우 OTF가 실제로 negative가 되는 spatial frequency가 존재한다. 이는 pahse reversal에 correspond 한다.
이러한 effect를 고려하기 위해 System에 대한 input이 다음에 의해 define 된 intensity image라고 가정하자.
$$I\left(x_{o}, y_{o}\right)=1+\cos \left(2 \pi \xi_{0} y_{0} x_{o}\right)$$
아래 그림에서와 같이 이 signal은 $y$ position에 의해 determine 되는 frequency로 $x$에서 periodic 하다(그 반대도 마찬가지이다). Image에서 아래로 이동하고 spatial frequency가 increase 함에 따라, contrast가 decrease 하는 것을 image에서 명확하게 볼 수 있다. Fringe contrast가 0이 되는 region도 있으며, OTF graph가 나타난 그림의 zero-contrast region 직후에는 실제로 negative가 된다.
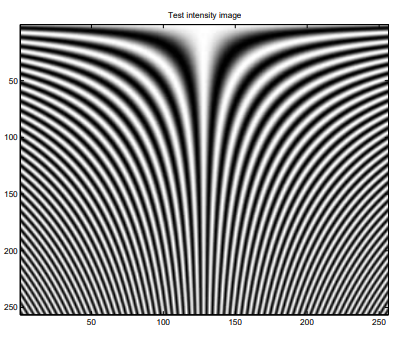
아래는 PSF 및 세 가지 다른 경우의 defocus aberration에 대한 output image이다.
'Optics > 이론' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lec 23. Performance Comparison between Coherent and Incoherent Imaging Systems (0) | 2021.08.31 |
|---|---|
| Lec 22. Coherent and Incoherent Imaging System/CTF/OTF/MTF/PSF (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| Lec 21. Coherence of Optical Fields (0) | 2021.08.30 |
| Lec 20. Physical Optics Description of Imaging System (0) | 2021.08.27 |
| Lec 19. Fourier Transforming Properties of Lenses and Gaussian Cavities (1) | 2021.08.26 |